When we think of common health issues, we often consider conditions like fatigue, digestive problems, skin rashes, or even joint pain. But did you know that these symptoms may have a deeper, underlying cause that isn’t always recognized in Western medicine? In Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), one such cause is internal dampness — a condition where excess moisture accumulates in the body, disrupting normal physiological functions.
While the concept of internal dampness might sound foreign, its symptoms can mirror common health problems that many people in the West experience. From digestive discomfort to fatigue, these signs can be found not only in Chinese medicine but also in Western medical diagnoses. Understanding the connection between the two can provide a more comprehensive approach to managing your health.
In this article, we’ll explore the 9 signs of internal dampness in the body and how they correspond to symptoms recognized in Western medicine. By understanding these symptoms and their causes, you can gain valuable insight into how your body might be signaling imbalances — and what you can do to address them.
Recognizing these signs can help you better understand your body and take steps to address internal dampness.
一、Oral
1.Bad Breath
- Dampness obstructs the spleen and stomach, causing digestive dysfunction. When food is not properly digested, dampness and food residue accumulate, leading to bad breath. This is more noticeable in the morning as digestion slows overnight, and the accumulation of dampness and food waste becomes more evident.
- Organs affected: Primarily the spleen and stomach. The spleen controls digestion and transformation; when dampness accumulates, it disrupts this process.
2.Dry Mouth
- Dampness should ideally nourish the body, but when it is excessive, it obstructs the spleen and stomach, causing the loss of body fluids. The spleen and stomach are unable to properly process fluids, leading to dry mouth and persistent thirst. Drinking water may not relieve this, as dampness blocks the body’s ability to absorb fluids.
- Organs affected: The spleen, stomach, and lungs. The spleen’s inability to properly transport fluids and the lungs’ inability to distribute qi result in dryness.
3.Thick and Greasy Tongue Coating
- The tongue coating is an important indicator of the body’s internal health. Excessive dampness accumulates in the spleen and stomach, causing digestive dysfunction and food stagnation. This leads to the formation of thick, greasy tongue coating, which is often white or yellow and mostly located at the back of the tongue. This reflects the inability of the body to expel the dampness.
- Organs affected: The spleen and stomach. Dampness obstructs the normal function of these organs, leading to thick and greasy tongue coating.
4.Bitter Taste in the Mouth
- A bitter taste in the mouth is often a sign of internal damp-heat. When dampness lingers in the body for too long, it turns into heat. Damp-heat obstructs the spleen and stomach, disrupting the normal flow of gastric qi. This results in a bitter taste, along with a yellow tongue coating, indicating internal damp-heat. The bitter taste is usually accompanied by dry mouth and constipation.
- Organs affected: The spleen, stomach, and liver. Damp-heat stagnates in these organs, leading to a bitter taste in the mouth.
Summary
- Bad breath is caused by dampness obstructing the spleen and stomach, leading to poor digestion and food stagnation, which disrupts the spleen and stomach’s transformation and transportation.
- Excessive dampness obstructs the metabolism of fluids, preventing them from being effectively absorbed and utilized, leading to dry mouth and persistent thirst.
- Dampness accumulates in the spleen and stomach, causing dysfunction in their transformation and transportation, resulting in a thick and greasy tongue coating.
- Internal damp-heat forms, where dampness combines with heat to obstruct the spleen and stomach, leading to disrupted gastric qi and a bitter taste in the mouth.
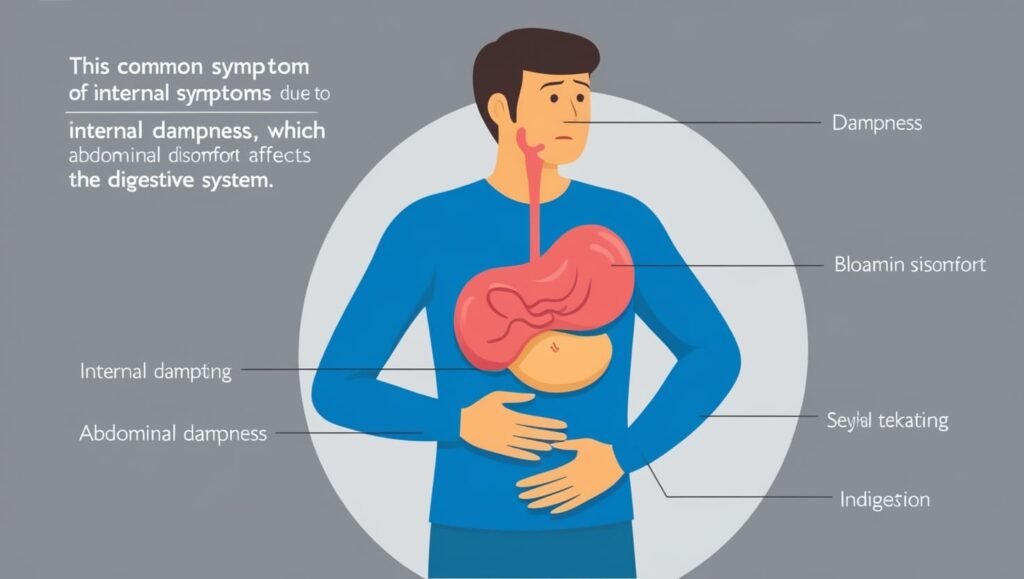
二、Digestive System Issues
For example, loose stools are a common sign of internal dampness interfering with the spleen’s function.
1.Loose Stools or Diarrhea
- When dampness accumulates, it obstructs the spleen and stomach, impairing their ability to transform and transport fluids. The spleen governs the transformation of water and dampness, and when dampness overwhelms it, it causes the retention of excess moisture, leading to loose stools, diarrhea, or stools that are sticky and hard to flush. This dysfunction in digestion results in poorly formed stools.
- Organs affected: The spleen and stomach. The spleen is responsible for the transportation of fluids, and when obstructed by dampness, it leads to digestive issues like loose stools.
2.Loss of Appetite
- Dampness stagnates in the spleen and stomach, impairing their ability to process food and fluids. The spleen is responsible for the digestion and transformation of food, and when dampness accumulates, the spleen’s ability to transport and transform nutrients is weakened. This leads to a reduced appetite and a decrease in food intake.
- Organs affected: The spleen and stomach. The spleen’s role in digestion is disrupted by dampness, leading to loss of appetite.
3.Chest Oppression
- When dampness accumulates, it obstructs the flow of qi, especially in the spleen and stomach, causing a blockage in the smooth circulation of qi and blood. Dampness tends to be heavy and turbid, leading to a feeling of oppression in the chest and difficulty breathing. This sensation of heaviness is often associated with stagnation in the chest area.
- Organs affected: The spleen, stomach, and lungs. Dampness obstructs the spleen’s qi and may also affect the lungs, leading to chest tightness and breathing difficulties.
4.Abdominal Bloating
- Dampness stagnates in the spleen and stomach, especially after meals, obstructing the digestive functions of these organs. This leads to bloating and the accumulation of gas in the abdomen. Dampness also hinders the spleen’s ability to transform food and fluids, causing food to stagnate in the digestive tract, which results in bloating, particularly after eating.
- Organs affected: The spleen and stomach. Dampness obstructs the spleen’s digestion and the stomach’s ability to process food, leading to bloating.
Summary
- Dampness obstructs the spleen and stomach, disrupting digestion and causing poor formation of stools.
- Dampness stagnates in the spleen and stomach, weakening their digestive function, leading to a decrease in appetite and food intake.
- Dampness obstructs the flow of qi, especially in the spleen and stomach, causing stagnation in the chest and difficulty breathing.
- Dampness obstructs digestion in the spleen and stomach, leading to the accumulation of food and gas in the abdomen, causing bloating.
The appearance of these symptoms reflects the interaction between the organs and the influence of dampness on the spleen and stomach. When dampness accumulates, it impairs the transformation and transportation functions of the spleen and stomach, leading to digestive issues such as loose stools, loss of appetite, chest oppression, and abdominal bloating. The accumulation of dampness not only disrupts digestion and absorption but also obstructs the smooth flow of qi and blood.
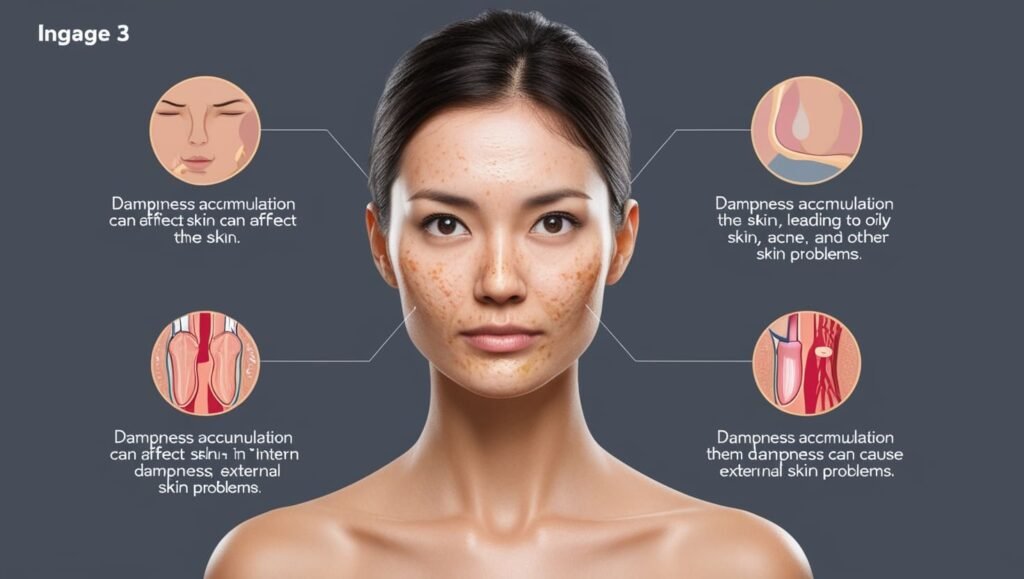

三、Skin and Hair Issues
Here is a detailed analysis of how heavy dampness causes skin and hair problems:
-
OilyHair
- When dampness accumulates in the body, it combines with heat to cause excessive secretion of sebum from the sebaceous glands. Dampness obstructs the flow of qi and blood, affecting the scalp’s metabolism, making it difficult for oil to be properly excreted, which results in oily hair, often accompanied by dandruff.
- Organs affected: The spleen and kidneys. When dampness is heavy in the spleen and stomach, it disrupts the flow of qi and blood, affecting the scalp and causing excess oil production.
-
Hair Loss
- Dampness is closely related to poor circulation of blood. When dampness obstructs the smooth flow of qi and blood, it results in insufficient blood supply to the scalp. Excessive dampness leads to a disharmony of qi and blood, which can cause hair loss, especially when dampness leads to an oily scalp.
- Organs affected: The kidneys, spleen, and liver. Dampness harms kidney essence, affecting the nourishment of hair follicles. Weak spleen qi leads to insufficient blood, and liver stagnation may also contribute to hair loss.
-
Premature Gray Hair
- Prolonged accumulation of dampness harms kidney qi. The kidneys store essence and are responsible for growth and development, including hair. Excess dampness affects the kidneys’ ability to store and circulate essence, resulting in premature gray hair. Dampness that stagnates in the body also weakens kidney function over time.
- Organs affected: The kidneys. When kidney essence is insufficient, hair growth and pigmentation are affected, and prolonged dampness exacerbates kidney qi deficiency.
-
Oily Skinon the Face
- When dampness accumulates in the body, it often leads to excessive oil production in the skin, especially on the face. Dampness impairs normal skin metabolism and may clog pores, leading to oily, shiny skin on the face.
- Organs affected: The spleen, stomach, and lungs. When the spleen and stomach’s ability to transform fluids is impaired, dampness affects the lungs, leading to the outward manifestation of oily skin on the face.
-
Eczema
- Dampness clogs the pores and the surface of the skin, which, when combined with the proliferation of dampness, can lead to symptoms of eczema such as itching, redness, and swelling. This is particularly common in humid environments, where the accumulation of dampness triggers eczema. Dampness can also weaken the skin’s immune function, leading to allergic reactions.
- Organs affected: The spleen and lungs. Dampness impedes the spleen’s transformation function and the lungs’ dispersing function, reducing the skin’s immunity and making it more susceptible to eczema.
-
Yellowish Complexion and Skin Spots
- When dampness accumulates over time, it impairs the spleen’s ability to transform and transport fluids, causing a lack of nourishment for the skin. This leads to a yellowish complexion and dull skin. In more severe cases, dark spots or pigmentation may develop. Dampness can also generate internal heat, further aggravating facial skin problems.
- Organs affected: The spleen, stomach, and liver. Impaired spleen function leads to poor fluid transformation, which affects the complexion. Liver stagnation can also exacerbate the formation of skin spots.
Summary
- Excessive dampness leads to overproduction of sebum, obstructs the flow of qi and blood, and disrupts scalp metabolism, resulting in oily hair.
- Dampness obstructs blood circulation, leading to insufficient blood supply to the scalp, and oily scalp due to dampness exacerbates hair loss.
- Prolonged accumulation of dampness harms kidney qi, leading to insufficient nourishment of hair follicles and premature gray hair.
- Accumulation of dampness causes excessive oil secretion in the skin, obstructing metabolism, leading to oily, shiny skin on the face.
- Dampness clogs pores, leading to eczema, especially in humid environments.
- Accumulation of dampness impairs the spleen and stomach, leading to poor nourishment of the skin, resulting in a yellowish complexion and skin spots.
These issues often point to the presence of internal dampness in the body.

四、Weight and Body Shape Issues
-
Fake Fat
Pseudo-obesity often results from internal dampness causing fluid retention and fat accumulation.When internal dampness is not properly expelled, it causes the stagnation of fluids and accumulation of fat in the body, resulting in “fake fat” or puffiness. This refers to looking overweight but having loose muscles without actual fat accumulation. When dampness is heavy, poor fluid metabolism causes a bloated appearance, leading to fat-like symptoms without true fat gain.
-
Swelling/Edema
Heavy dampness often leads to swelling, especially around the eyes, lower legs, and hands or feet. Dampness obstructs the normal circulation of fluids in the body, causing localized fluid retention and swelling, which is often most noticeable in the morning after waking up.
-
Sagging Eye Bags
Prolonged dampness in the body can lead to persistent swelling in the eye area, causing the eye bags to sag. The stagnation of dampness in the eye area results in puffiness and looseness of the tissue, making the bags under the eyes appear droopy. This is especially noticeable in seasons with high humidity or in damp environments.
These weight and body shape issues are common manifestations of internal dampness. Dampness affects the metabolism and circulation of fluids in the body, leading to edema, swelling, and other related problems, thus influencing both physical appearance and overall health.
五、Eye and Facial Issues
The following is a detailed analysis of how heavy dampness causes eye and facial problems:
-
DarkCircles under the Eyes
- Dark circles can result from poor blood circulation caused by internal dampness.When dampness accumulates in the body, it disrupts the flow of qi and blood, particularly in the spleen and stomach. This causes poor circulation, especially around the eyes, leading to a lack of qi and blood in the eye area. The stagnation of dampness also worsens water retention, contributing to dark circles or puffiness around the eyes.
- Organs affected: The spleen, kidneys, and liver. Dampness in the spleen and stomach leads to poor qi and blood circulation, while stagnation of dampness affects kidney essence and liver function, resulting in poor circulation around the eyes.
-
Dry Eyes
- When dampness accumulates, it disrupts the body’s fluid metabolism, causing an imbalance in the distribution of body fluids. Dampness obstructs normal fluid circulation, leading to insufficient moisture in the eyes. This results in dryness, irritation, and blurred vision. Dampness can also affect the function of the organs around the eyes, exacerbating discomfort.
- Organs affected: The spleen, kidneys, and liver. Dampness obstructs the spleen and stomach’s ability to regulate fluid metabolism, preventing adequate moisture from reaching the eyes. It also disrupts liver function, which contributes to the lack of nourishment for the eyes.
Summary
- Dampness causes poor circulation of qi and blood, leading to dark circles or puffiness around the eyes due to stagnation of blood flow.
- Dampness disrupts fluid metabolism in the body, leading to insufficient moisture for the eyes, resulting in dryness, irritation, and blurred vision.
The accumulation of dampness in the body clearly affects the eyes and face, particularly through its impact on the spleen, kidneys, and liver, which causes poor circulation and insufficient moisture in the eyes, leading to symptoms such as dark circles, puffiness, and dry eyes.
六、Mental and Neurological Issues
The following is a detailed analysis of how heavy dampness causes mental and nervous system problems:
-
Fatigue
- When dampness accumulates, it impairs the functioning of the spleen and stomach, leading to poor circulation of qi and blood. This stagnation of dampness obstructs the generation and flow of qi and blood, resulting in fatigue, a feeling of heaviness, and difficulty focusing. The spleen’s inability to properly transform and transport fluids further contributes to the sensation of tiredness.
- Organs affected: The spleen and stomach. Dampness in the spleen and stomach disrupts the normal transformation and transportation of qi and blood, leading to a deficiency in qi and blood, causing fatigue.
-
MentalFatigue/Depression
- Dampness obstructs the flow of qi and blood, leading to deficiencies in both, which in turn affect the heart and mind. Stagnation of dampness results in sluggish thinking, difficulty concentrating, and even emotional symptoms such as low mood, anxiety, or depression. The accumulation of dampness prevents the nourishment of the mind, leading to a feeling of mental fatigue or a lack of vitality.
- Organs affected: The spleen and heart. Dampness disrupts the spleen’s function of transformation and transportation, leading to qi and blood deficiency, which results in insufficient nourishment to the heart and mind, causing mental fatigue and depression.
-
Insomnia
- Insomnia may occur as internal dampness disrupts the body’s balance.Dampness disturbs the heart and mind, affecting the transformation and transportation of the spleen and stomach, leading to an imbalance in qi and blood. When dampness accumulates in the body, it often combines with heat, disturbing the heart’s spirit and causing symptoms like insomnia, vivid dreams, and frequent waking at night. The stagnation of dampness prevents the balance of qi and blood, disrupting normal neurological function and leading to sleep disturbances.
- Organs affected: The spleen, stomach, and heart. Dampness in the spleen and stomach disrupts the normal transformation and transportation of qi and blood, and damp-heat accumulation disturbs the heart, leading to insomnia.
Summary
- Dampness obstructs the spleen’s function, causing poor circulation of qi and blood, leading to fatigue, heaviness, and difficulty concentrating.
- Dampness obstructs the flow of qi and blood, leading to a lack of mental vitality, difficulty focusing, and symptoms of depression or low mood.
- Dampness disturbs the heart and mind, causing insomnia, vivid dreams, and frequent waking during the night.
The accumulation of dampness clearly affects the mental and neurological system, especially through its impact on the spleen, stomach, and heart, leading to poor circulation of qi and blood, and causing symptoms such as fatigue, mental fatigue, and insomnia.
七、Respiratory System Issues
-
Excessive Phlegm
When dampness stagnates in the lungs, it leads to the production of excess phlegm. With heavy dampness, the phlegm becomes thick and sticky, making it difficult to expel. The phlegm accumulates in the respiratory tract, making it hard to clear the throat and causing breathing difficulties or coughing.
-
Coughing
Dampness affects the health of the respiratory tract, making coughing more likely. Especially when dampness is heavy, the symptoms of coughing become more severe. Dampness not only makes the airways more sensitive but also exacerbates phlegm production, resulting in persistent dry cough or productive cough. When the dampness is excessive, coughing may also be accompanied by chest tightness or shortness of breath.
These respiratory issues often point to the accumulation of internal dampness in the lungs.These respiratory system issues are related to the stagnation of dampness in the lungs and respiratory tract. Dampness hinders the smooth flow of air, leading to symptoms such as coughing and excessive phlegm, which affect normal respiratory function.
八、Reproductive System Issues
-
Vaginal Dampness and Odor
- When dampness accumulates, it obstructs the spleen and kidneys, affecting the normal function of the reproductive system. Dampness tends to accumulate in the lower abdomen (lower burner), causing vaginal dampness, unpleasant odor, and possibly itching. The stagnation of dampness obstructs the circulation of qi and blood, leading to the accumulation of damp-heat in the local area, which affects vaginal health.
- Organs affected: The spleen and kidneys. Dampness in the spleen obstructs the spleen’s function of transformation, and stagnation of dampness and heat affects kidney function, leading to vaginal dampness and odor.
-
ScrotalDampness and Odor
- In men, excessive dampness can obstruct the spleen and kidneys, particularly in the lower abdomen (lower burner), causing scrotal dampness and odor. The accumulation of dampness and heat may lead to local inflammation or infection, impacting male reproductive health.
- Organs affected: The spleen and kidneys. Dampness in the spleen obstructs the transformation function, and stagnation in the kidneys and lower abdomen leads to scrotal dampness and odor.
-
Loss of Sexual Desire
- Dampness obstructs the spleen and kidneys, causing a deficiency of qi and blood, which affects normal sexual function. When dampness accumulates, it weakens the spleen and stomach, which in turn affects the kidneys and leads to a deficiency in kidney essence. This results in a decreased libido or sexual disinterest.
- Organs affected: The spleen and kidneys. Dampness obstructs the normal transformation of qi and blood by the spleen and affects the kidneys, leading to a decrease in sexual desire.
- Abnormal
Vaginal Discharge
- Abnormal discharge may result from the presence of internal dampness or damp heat.When dampness and damp-heat accumulate in the body, especially in the lower burner (lower abdomen), it can cause an increase in vaginal discharge, often with an unpleasant odor. Damp-heat obstructs the transformation function of the spleen, affecting normal fluid metabolism and leading to abnormal discharge.
- Organs affected: The spleen, kidneys, and ren (Conception) vessel. Dampness and damp-heat obstruct the transformation function of the spleen and accumulate in the lower burner, causing abnormal discharge and odor.
Summary
- Dampness obstructs the spleen and kidneys, leading to vaginal dampness, odor, and possible itching.
- Dampness accumulates in the spleen and kidneys, causing scrotal dampness and odor.
- Dampness obstructs the spleen and kidneys, leading to decreased libido and sexual disinterest.
- Excessive dampness and damp-heat disrupt the transformation of the spleen, leading to abnormal vaginal discharge with an unpleasant odor.
The accumulation of dampness clearly affects the reproductive system, especially through its impact on the spleen and kidneys, leading to vaginal and scrotal dampness, decreased libido, and abnormal discharge.
九、Other Issues
The following is a detailed analysis of other common symptoms caused by dampness:Other symptoms of internal dampness include dizziness and joint pain.
1.Dizziness
- When there is excessive dampness, it obstructs the normal flow of qi and blood. Dampness hinders the circulation of blood, particularly affecting the brain’s blood supply, which can lead to dizziness, a heavy feeling in the head, and even snoring. The stagnation of dampness can also impair the flow of qi and blood to the head.
- Organs affected: The spleen, liver, and kidneys. Dampness obstructs the spleen’s function of qi transformation and weakens the circulation of qi and blood, also potentially impacting liver and kidney function.
2.Joint Pain
- When dampness accumulates, it obstructs the joints, leading to symptoms like joint soreness, stiffness, and pain. Dampness is sticky and obstructs the circulation of qi and blood in the joints, which causes pain. Additionally, weather changes or a humid environment can worsen these symptoms, especially for older individuals or those with weaker joints.
- Organs affected: The spleen, kidneys, and meridians. Dampness impedes the transformation function of the spleen and can invade the joints through the meridians, causing stagnation of qi and blood, leading to joint pain. Those with kidney deficiency are particularly prone to dampness affecting the joints.
Summary
- Excessive dampness obstructs the circulation of qi and blood, affecting the brain’s blood supply, leading to dizziness and a heavy head.
- Dampness obstructs the joints, causing soreness, stiffness, and pain, which can worsen in humid environments or with weather changes.
Dampness affects the circulation of qi and blood, the functions of the organs, and the supply of qi and blood to the local areas, leading to symptoms like dizziness and joint pain.